In the pursuit of a more sustainable and environmentally responsible future, the construction industry is undergoing a significant transformation. One of the most promising advancements in this sector is Offsite construction, which is gaining momentum for its modular sustainability benefits, offering the ability to reduce environmental impact while maintaining high-quality construction standards.
The Waste and Resources Action Programme (WARP) has unveiled some staggering insights. When we look at modular construction versus traditional building methods, the environmental benefits become clear. The production of a modular building consumes up to 67% less energy when compared to its traditional counterpart.
Modular projects also have the ability to wrap up construction much faster, resulting in significant reduction in on–site energy consumption. WARP anticipates that embracing modular construction could usher in a 90% reduction in materials used. This sustainable lifecycle approach not only makes them durable and reusable, but also aligns with the circular construction methodology, which strives to minimize waste and reduce our environmental footprint. In essence, modular construction is a pivotal player in building a greener, more sustainable future.
Sustainable Advantages of Modular Construction
In a world where sustainability goals are becoming increasingly ambitious and urgent, the building industry is in need of innovative solutions. Modular construction enthusiasts argue that this cutting-edge approach holds the potential to deliver superior environmental and social sustainability benefits compared to traditional construction methods.
The impressive sustainability advantages associated with modular construction include:
- Significant Waste Reduction
- Lower Carbon Footprint
- Relocate, Renovate, and Repurpose
- Greater Energy Efficiency
Minimizing Material Waste in Modular Construction
In the evolving landscape of sustainability in the construction industry, modular construction stands out as a game-changer, offering various sustainability benefits. Research has consistently underscored the construction sector’s significant role in waste generation and environmental impact, with concerns ranging from greenhouse gas emissions to land usage for waste and landfilling.
Off-site prefabrication and assembly have shown promise in being a solution to reducing construction waste, and modular construction is at the forefront of this paradigm shift. A recent research paper delves into the quantifiable differences between off-site modular construction and traditional on-site methods across various sustainability criteria. By examining waste generations rates, this study reveals that modular construction can potentially reduce overall waste weight by an outstanding 83.2%, translating to 47.9% cost reduction in waste management for large-scale structures.
In a study conducted by Quale et al., a comparison was made between a traditional house and a four-plex house constructed using similar materials. The findings of the study revealed that on-site construction exhibited environmental impacts ranging from 20% to 70% higher than those associated with modular construction.
The 2022 FIFA World Cup in Qatar includes seven state-of-the-art stadiums, with one of them set to entirely disappear after the month-long event. Stadium 974 was a world cup stadium built using relocatable modular structures. The goal was to disassemble the stadium after the 2022 football tournament and either reassemble it in a new location or repurpose it into a series of smaller venues. Using modular structure led to reduced expenses, faster construction, and significantly cut down on material wastage.
Contributing to a Circular Economy – Repurpose & Reuse
Towards the end of a building’s lifecycle, modular structures can offer an opportunity for reuse. Instead of resorting to the conventional demolition process, which typically results in the disposal of building materials in landfills, modular units can be carefully disassembled, disconnected, and transported away from the construction site. These modules frequently find a second life on other projects, significantly diminishing the demand for fresh raw materials and energy typically required to construct an entirely new building. This sustainable practice exemplifies the circular economy concept, where resources are maximized, and waste minimized in the construction industry.
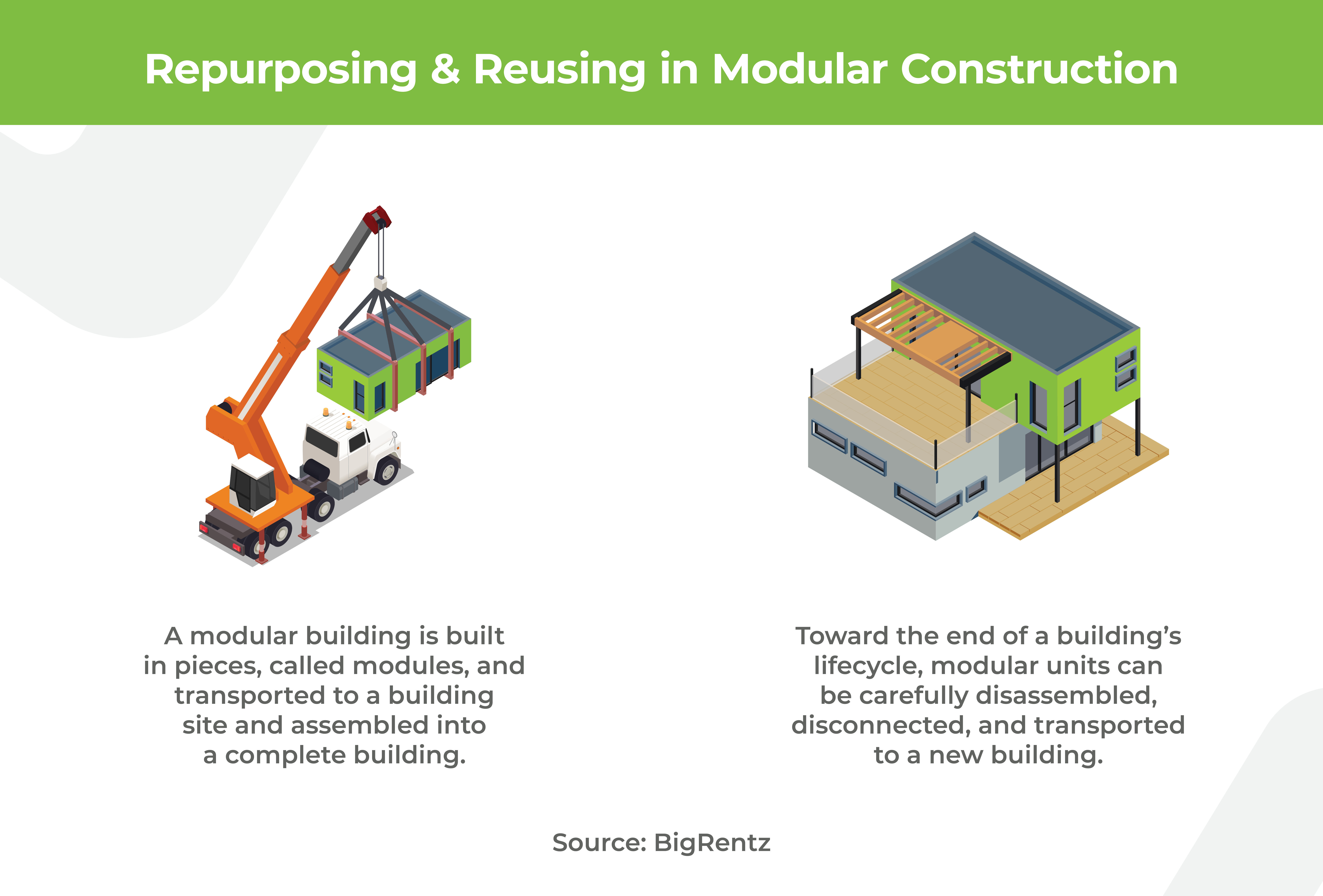
In contrast to traditionally constructed buildings, modular structures offer the advantage of adaptability. These prefabricated units adhere to the same building codes and standards, providing enduring functionality similar to permanent construction. Repurposing modular buildings in different locations not only mitigates the consumption of materials and energy during their initial construction but also diminishes the demand for fresh materials in subsequent applications.
Sustainability within modular construction holds immense promise as a solution for the future of the building industry. Its ability to reduce energy consumption, lower waste generation, and enable adaptability aligns perfectly with the growing urgency to meet ambitious sustainability goals. As we strive for a more environmentally responsible world, modular construction stands out as a key player in shaping a greener, more sustainable future for the construction sector.
Embrace modular construction for a sustainable tomorrow! Contact us to collaborate and partner for a sustainable future.



